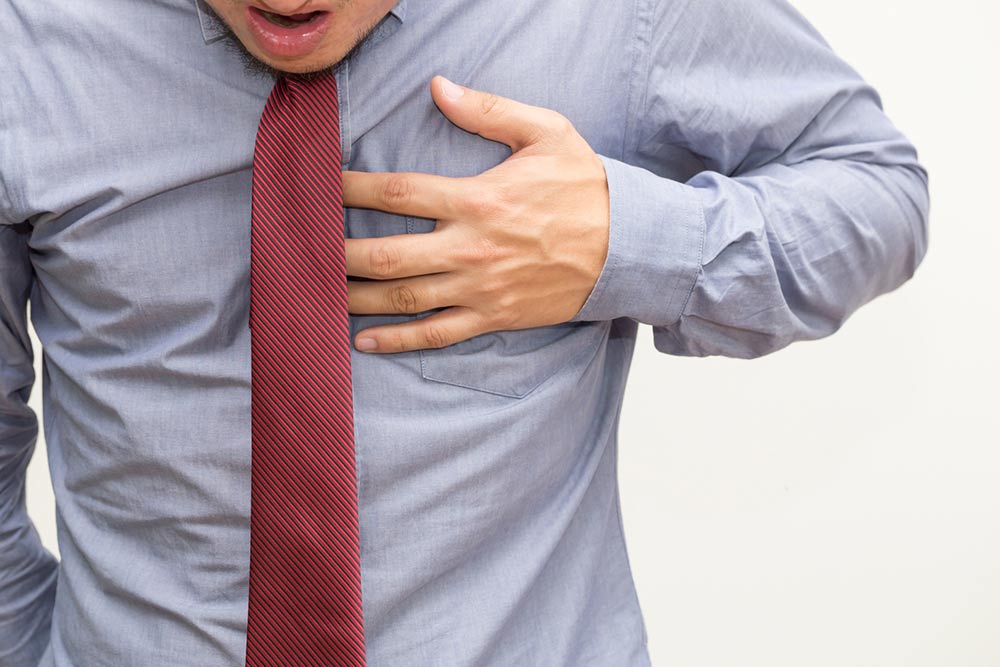
While not all heart problems have clear symptoms, many of them are often preceded by a series of early warning signs. Being aware of these early signs can be useful in seeking diagnosis and treatment on time. This is crucial since most heart diseases can be easily avoided if detected and treated before the symptoms become too severe. Those with increased risk factors need to keep an eye on these early warning signs of heart disease. 1. Experiencing pain in the chest Most people often have chest pain, which is one of the most common early warning signs of heart disease. It is not just an oncoming heart attack that causes severe chest pain, but many other heart-related problems. For example, a person may feel a shooting pain in their chest when they exert themselves. However, the pain may go away when they are at rest. This is usually a sign of angina. Whenever one experiences chest pain along with the feeling of extreme unease, it is best to consult a doctor as soon as possible. 2. Feeling nauseated Nausea can be an early sign of a lot of health problems. Yet, many people ignore it, assuming it will go away.